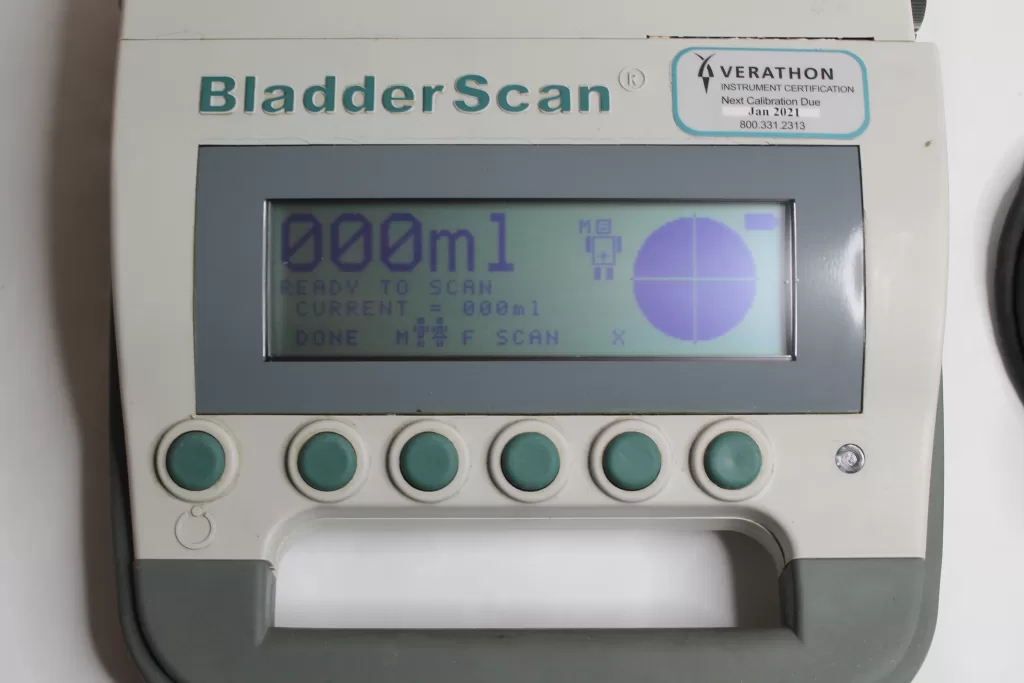
Testing the Verathon BladderScan Portable Bladder Scanner Model BVI 3000 0570-0090 involves a series of steps to ensure its accuracy and functionality. Here’s a concise guide to testing this device:
- Initial Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the device for any physical damage, loose connections, or signs of wear. Ensure all cables, probes, and components are intact and in good condition.
- Power Up and Calibration: Power on the Bladder Scanner and allow it to undergo its self-diagnostic routine. Once powered up, calibrate the device following the manufacturer’s instructions. Calibration ensures accurate measurements.
- Probe Preparation: Properly attach the probe to the device according to the user manual. Ensure the probe is clean and free from any debris or damage that could affect its functionality.
- Test Scans on Simulated Bladders: Perform test scans on simulated or phantom bladders, often provided by the manufacturer for testing purposes. Ensure the bladder is properly filled to mimic real patient conditions.
- Scanning Procedure: Place the probe gently on the simulated bladder’s surface, ensuring it makes full contact without excessive pressure. Follow the device’s instructions for scanning, which may involve aiming the probe correctly and holding it steady during the scan.
- Measurement Accuracy Check: Verify the accuracy of the measurements provided by the scanner against known volumes in the simulated bladder. Compare the device’s readings with the actual volumes to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Image Quality and Data Display: Evaluate the image quality displayed on the device’s screen. Check for clarity, visibility of bladder contours, and accurate measurement data displayed. Ensure the information is easily readable and understandable.
- Functional Tests: Perform various functions and modes available on the scanner, including different scanning modes or measurement options, to ensure the device operates as intended.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Document the test results, any issues encountered, and the corrective actions taken during the testing process. Maintain records for future reference and compliance purposes.
- Quality Control and Compliance: Adhere to any regulatory standards or quality control procedures specific to the use and testing of medical devices, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.